Carotid Artery Disease
Overview of Carotid Artery Stenosis
OVERVIEW
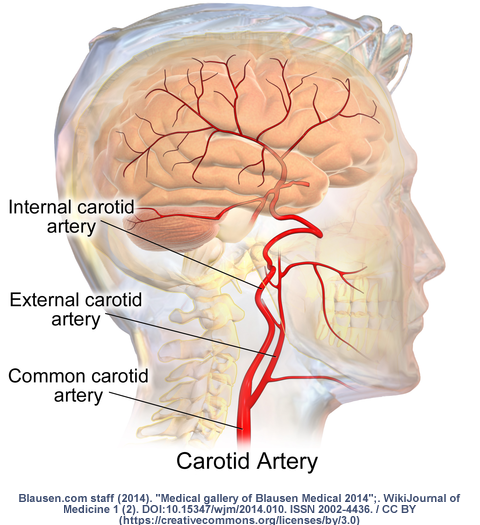
The carotid arteries are two large blood vessels that supply oxygenated blood to the large, front part of the brain. The common carotid arteries (CCA), located on both sides of your neck, divide into two vessels. These vessels are called the external carotid arteries (ECA) and the internal carotid arteries (ICA). These arteries also bring blood to your face.
CAROTID ARTERY DISEASE
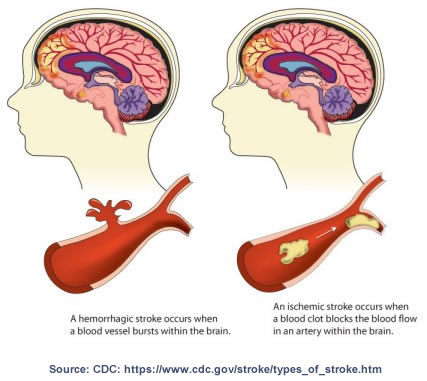
This disease occurs when fatty deposits, also known as plaques clog the carotid arteries. This blockage increases your risk of stroke, a medical emergency that occurs when the blood supply to the brain is interrupted or seriously reduced. Stroke is the most common cause of death and the leading cause of permanent disability in the U.S.
SYMPTOMS
Unfortunately, there may be little to no symptoms until the blockage becomes severe, which is why strokes typically happen out of the blue. Your doctor can often detect signs of blockage by listening to your artery with a stethoscope. This is why it is important to get checked out periodically, specially, if your lifestyle is less than healthy. Please review the risk factors below. Mini-strokes, also known as TIA or transient ischemic attack, can also be a sign of blocking in your arteries. TIAs are like stroke, but much shorter in duration and often the symptoms go away after a short period.
Symptoms of a stroke or TIA could include:
- Sudden numbness or weakness of the face, arm or leg, especially on one side
- Sudden confusion or dizziness
- Sudden trouble speaking or understanding
- Sudden trouble seeing in one or both eyes
- Sudden trouble walking, loss of balance or coordination
- Sudden, severe headache with no known cause
- Sudden trouble swallowing
You must not ignore these signs and must contact a doctor immediately. Your doctor may be able to identify any warning signs. If you believe you’re experiencing a transient ischemic attack, consider it a medical emergency because it is impossible to predict if it will progress into a major stroke. Your chances of survival increase the sooner your seek medical attention.
RISK FACTORS
Some of the risk factors include:
- Age
- Smoking
- High blood pressure
- High cholesterol
- Obesity
- Diabetes
- Sedentary lifestyle
- Family history
Information on this site should not be used as a substitute for talking with your doctor. Always talk with your doctor about diagnosis and treatment information.
